Known issues¶
This is a list of known possible issues with HiSPARC stations. For each problem some steps are given which can be followed to determine if that problem is indeed occuring on your station. Possible Nagios Service warnings that might alert you to the problem are noted.
Here are filters to only show problems which cause a certain Nagios warning: Buffer size, CPU Load, Drive Space, EventRate, Labview Usage, Memory Usage, StorageGrowth, StorageSize, TriggerRate, Uptime.
Note
Multiple issues can cause the same Nagios warning.
Each problem described below has the following fields:
| First Sign: | Explaining how you will probably notice the problem. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Nagios warnings that can be triggered. |
| Determination: | This is a small guide explaining how to make sure that the problem being described is what you are experiencing. |
| Solution: | How to solve it. |
| Effects: | The effects of this problem. |
Software¶
This sections concerns itself with issues related to the HiSPARC station-software.
HiSPARC Monitor does not start¶
Missing directory¶
| First Sign: | When the STARTHiSPARCSoftware program runs and the other programs (HiSPARC DAQ and Updater) start normally but the HiSPARC Monitor does not appear or closes instantly. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | EventRate, StorageGrowth, StorageSize, TriggerRate, and possibly Buffer size |
| Determination: |
|
| Solution: | Create the missing hsmonitor directory in hisparc/persistent/data. |
| Effects: | The missing directory causes the HiSPARC Monitor to be unable to store events in its SQLite database, preventing it from sending events to the Nikhef datastore. Note that the HiSPARC DAQ should be unaffected. No events should be lost, the DAQ will store events in its MySQL database until the hard disc fills up. |
Hard Disc Space¶
To many logs¶
| First Sign: | Nagios warning about Disc Space. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Drive Space |
| Determination: |
|
| Solution: | Remove all logs from the src directory except for the current one (present date in dd-mm-yyyy.log). Select all (ctrl + a) logs in hisparc/persistent/logs/src. Deselect the current one (ctrl + click). Remove them using shift + delete (to bypass the Recycle Bin) |
| Effects: | If the disc is full the HiSPARC daq can not store events in the database, preventing the station from storing more events. |
To many updaters¶
| First Sign: | Nagios warning about Disc Space. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Drive Space |
| Determination: |
|
| Solution: | Remove all userUnpacker and adminUpdater files except the newest ones. Do this by selecting them and pressing shift + delete to remove them directly. |
| Effects: | If the disc is full the HiSPARC daq can not store events in the database, preventing the station from storing more events. |
HiSPARC DAQ Errors¶
Can not connect to buffer¶
| First Sign: | Red LED in HiSPARC DAQ |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | From the Start menu start odbcad32.exe. Check if the hisparc buffer is there. |
| Solution: | |
| Effects: | The HiSPARC DAQ will not be able to store events. |
Not in DAQ Mode¶
| First Sign: | |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Look at the program HiSPARC DAQ, see if the button in the middle shows ‘DAQ Mode’. |
| Solution: | Click the ‘DAQ Mode’ button in the HiSPARC DAQ. |
| Effects: | When the HiSPARC DAQ is not in DAQ Mode it will not store triggered events. |
Error in HiSPARC Monitor¶
Malformed HisparcII.ini¶
| First Sign: | Errors in the HiSPARC Monitor: Uncatched exception in job: need more than 1 value to unpack. Restarting... |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Check for blank lines in the file hisparc/persistent/configuration/HisparcII.ini. |
| Solution: | Remove any blank lines from HisparcII.ini |
| Effects: | Errors in the HiSPARC Monitor and no TriggerRate updates for Nagios. |
Time difference to large¶
| First Sign: | Errors in the HiSPARC Monitor: Uncatched exception in job: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'difference too large'. Restarting... |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Check for the text difference to large in hisparc/persistent/configuration/HisparcII.ini. |
| Solution: | Check the PC time, make sure that it is set to the current time. Check the GPS settings, make sure that it is working and showing the correct GPS time. |
| Effects: | Errors in the HiSPARC Monitor and no TriggerRate updates for Nagios. |
400 Bad Request¶
| First Sign: | Errors in the HiSPARC Monitor: Error Uploader: .. Return code: 400 |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | StorageSize, TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Ensure that all required variables are being uploaded: station_id, password, data and the checksum. |
| Solution: | Check that the station number and password are entered correctly in the configuration file: hisparc/persistent/configuration/config.ini. |
| Effects: | No data will be uploaded. |
Access denied for MySQL buffer¶
| First Sign: | Error in Nagios: Buffer size: Access denied for user 'buffer'@'localhost' |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Buffer size |
| Determination: | Check if the file hisparc/user/diagnosticchecks/checks.py contains only one path to a CONFIG_INI: CONFIG_INI = "../../user/hsmonitor/data/config.ini". |
| Solution: | Open the file hisparc/user/diagnosticchecks/checks.py in a text editor like NotePad and add the following line after the line starting with CONFIG_INI = "../..: CONFIG_INI2 = "../../user/hsmonitor/data/config-password.ini". Finally several lines later is the following code: config.read(CONFIG_INI), replace this by: config.read([CONFIG_INI, CONFIG_INI2]). Save the file. |
| Effects: | Nagios can not monitor the Buffer size. |
GPS¶
Firmware not loaded¶
| First Sign: | No GPS appears in DSP Mon |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | This only occurs with HiSPARC III electronics when their firmware is not yet loaded, which is indicated by all LEDs on the unit being on. |
| Solution: | Start the HiSPARC DAQ to load the firmware into the HiSPARC electronics. |
| Effects: | No GPS recognized by DSP Mon. |
COM Port to high¶
| First Sign: | The GPS date attatched to events is very inaccurate, like ~1999 or ~2019. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: |
|
| Solution: | Lower the COM Port Number, by direct reassignment, use the com_port_reassign utility. |
| Effects: | No GPS recognized by DSP Mon, this causes data to get dates like 1999 or 2019, making the data unusable. |
No antenna connected¶
| First Sign: | The GPS get no satelite signals, seen in the Satelites tab of the HiSPARC DAQ. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | Open DSP Mon and check the LED status of the Antenna Open. It will be yellow while some of the other LEDs are green. Also all Signal Values (SV) will be 0. |
| Solution: | Check the GPS cable for kinks or cuts, also check if the antenna is still properly attached. Once fixed the SV should rise and turn green, as well as the Antenna Open status. |
| Effects: | Makes the GPS unable to determine the correct date. Is falls back to some other date like 1999 or 2019, making the data unusable. |
Time offset¶
| First Sign: | No coincidences with nearby stations. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | Open DSP Mon and check if the timing for the GPS is set to UTC or GPS, it should be GPS. |
| Solution: | Set the GPS Timing to use GPS time. |
| Effects: | There is a difference of ~16 seconds between GPS en UTC time, resulting in offset timestamps if the wrong setting is chosen. |
Uploading¶
Proxy not set¶
| First Sign: | No data is uploaded, the local storage fills with events. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | StorageSize |
| Determination: | Run Diagnostics (LocalDiagnosticTool in older versions) to check if a proxy is required. |
| Solution: | Run Diagnostics (LocalDiagnosticTool in older versions) to check Proxy settings, if it finds proxy settings for the system it can use these to configure them for Python. Press the Write Config. |
| Effects: |
Firewall¶
Incoming firewall rules¶
| First Sign: | All active Nagios checks are critical. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Host, Buffer size, CPU Load, Drive Space, Labview Usage, Memory Usage, Uptime |
| Determination: | All of the above Nagios services are crtitical eventhough the software is running properly. |
| Solution: |
|
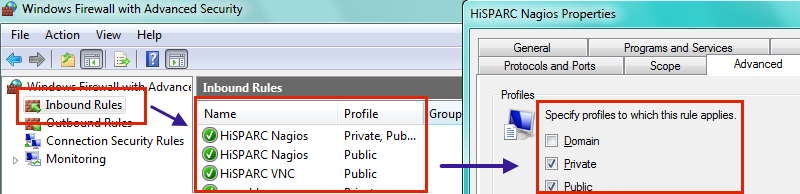
| Effects: | Nagios can not monitor the PC status, VNC may also be blocked. |
|---|
VPN blocked¶
| First Sign: | All Status indicators on Nagios are CRITICAL. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | Host, Buffer size, CPU Load, Drive Space, EventRate, Labview Usage, Memory Usage, StorageGrowth, StorageSize, TriggerRate, Uptime |
| Determination: | Run Diagnostics (LocalDiagnosticTool in older versions) to check the VPN status. |
| Solution: | Open TCP port 443 in the firewalls. |
| Effects: | Nagios will be unable to check the status of all services. Moreover, the HiSPARC support will be unable to log into the PC remotely to assist in case of problems. |
Web blocked¶
| First Sign: | No data is uploaded, the local storage fills with events. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | StorageSize |
| Determination: | Try opening a website in a browser on the detector PC, preferably www.nikhef.nl, if this fails then web traffic is blocked. If the browser has no problems, then look at the Proxy not set issue. |
| Solution: | Open port 80 in the firewalls |
| Effects: | The Uploader of the HiSPARC Monitor uses a HTTP POST Request to send data to our datastore, but this will be blocked if port 80 is closed. |
.exe blocked¶
| First Sign: | An update is available but the software can not download it. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | Try opening the link to the updater, shown in the HiSPARC Updater, in a webbrowser. If this fails then .exe files are probably blocked by the network. |
| Solution: | Allow downloading of .exe files through the firewall. |
| Effects: | The Updater will see there is an update and quit the HiSPARC DAQ. However when the update fail it will restart the HiSPARC software, but then see there is an update and try again, it will be stuck in this loop. |
Hardware¶
This sections concerns itself with issues related to the HiSPARC electronics and hardware.
Bad signals¶
Bad power supply¶
| First Sign: | HiSPARC DAQ might frequently loose the connection to the HiSPARC electronics or there will be fluctuations (sine) over the signal. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | Replace the power supply with a new one and see if the problem disappears. |
| Solution: | Replace the power supply. |
| Effects: |
Light leak¶
| First Sign: | Many small peaks (short pulses) in the signals in the HiSPARC DAQ, also the number of events will increase during day time (due to sunlight) |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Cover the detector with a light-tight blanket or foil. Now the extra peaks should disappear. |
| Solution: | Patch the light-leaking parts with new foil/tape. |
| Effects: |
Bad PMT base¶
| First Sign: | The current for one of the PMTs is very high (above 15 mA). |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | |
| Determination: | Look in the HiSPARC DAQ at the current used by the PMTs. If this is above 15 mA something if probably wrong. |
| Solution: | Try lowering the High Voltage on the PMT, or turning it off for a day. If that does not help it may need to be replaced, contact your cluster coordinator. |
| Effects: | The PMT will not function properly. |
No Devices Found¶
Connect to power¶
| First Sign: | HiSPARC DAQ is unable to connect to the HiSPARC electronics. |
|---|---|
| Nagios: | EventRate, StorageGrowth, StorageSize, TriggerRate |
| Determination: | Start the HiSPARC DAQ, it will show a message that no device is found. Check if the LEDs on the HiSPARC electronics box are lit. |
| Solution: | Connect the HiSPARC electronic box via the provided Power supply to a power outlet. |
| Effects: | No data can be taken. |
